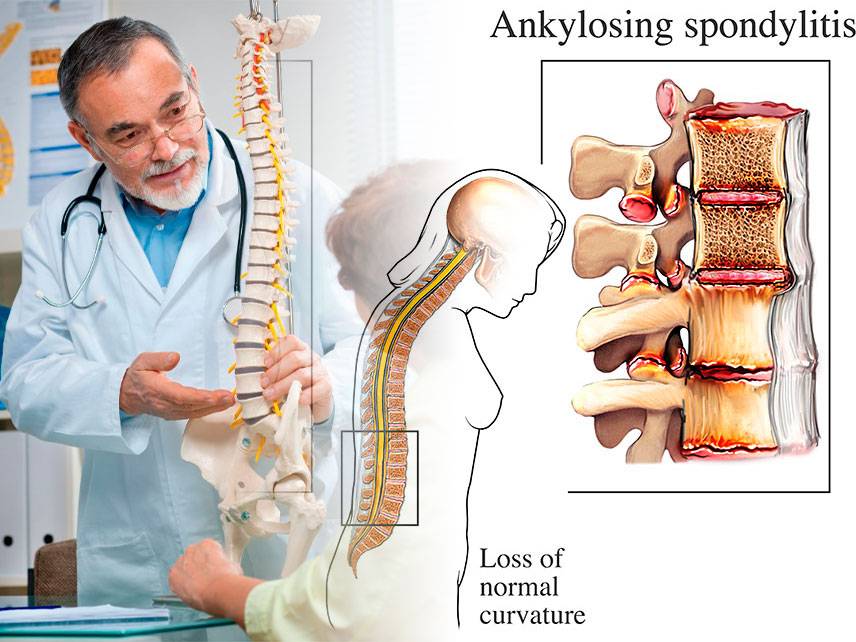
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, inflammatory disorder of the spine and the sacroiliac joints, which are located at the base of the spine. It is a type of arthritis, which causes the vertebrae to fuse together, leading to a rigid spine. AS is usually a progressive disease, meaning that symptoms may worsen over time.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis may include:
-
Lower back pain and stiffness
-
Stiffness and pain in the hips, buttocks, and thighs
-
Difficulty standing up straight
-
Loss of flexibility in the spine
-
Pain that is worse in the morning and after periods of inactivity
-
Fatigue
-
Pain and swelling in other joints, such as the knees, ankles, feet, and shoulders
-
Uveitis (inflammation of the eye)
Causes
The exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis is not known, but it is believed to be related to genetics and the body’s immune system. People with a family history of AS are more likely to develop the condition.
Risk Factors of Ankylosing spondylitis
Risk factors for ankylosing spondylitis include:
-
Family history of AS
-
Being male
-
Being of Northern European descent
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent ankylosing spondylitis, but leading a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk. Getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can all help to reduce the risk of developing AS.
Diagnosis
Ankylosing spondylitis can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. A doctor will usually take a medical history, perform a physical exam, and order blood tests and X-rays to help make a diagnosis.
Treatment of Ankylosing spondylitis
Treatment for ankylosing spondylitis usually involves a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and stiffness, improve mobility, and maintain quality of life. Common treatments for AS include:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
-
Steroids
-
Biologics
Coping and Support
Living with ankylosing spondylitis can be difficult, but there are ways to cope with the condition. Joining support groups and talking to others who have AS can be a great source of comfort and understanding.
Complications of Ankylosing spondylitis
There are potential complications of ankylosing spondylitis, including:
-
Respiratory problems due to the spine becoming more rigid
-
Inflammation of other joints
-
Uveitis (inflammation of the eye)
Living with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Living with ankylosing spondylitis can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the condition. Regular exercise, good nutrition, and stress management can help to improve symptoms and maintain quality of life. It is important to stay in close contact with your doctor and to follow their treatment plan.