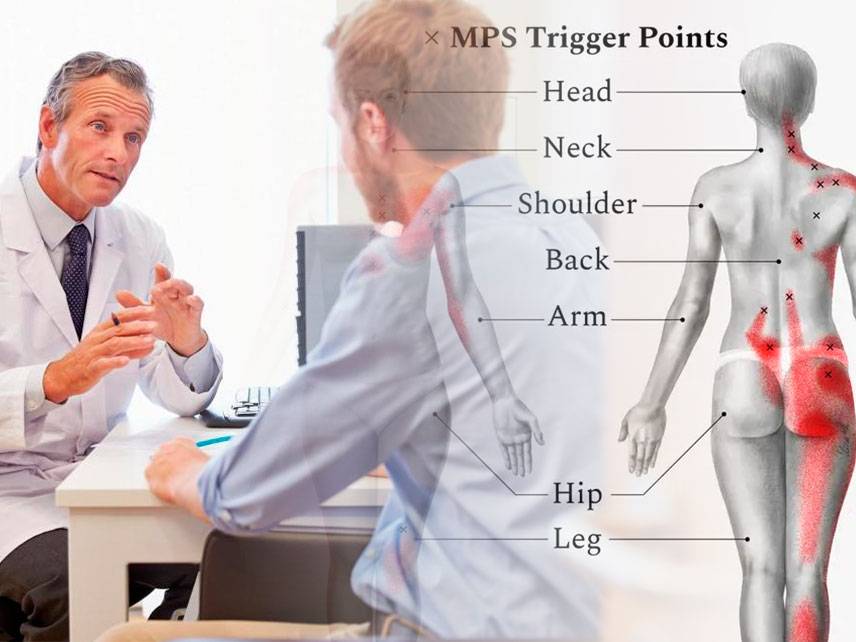
Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic condition that causes pain and tenderness in the muscles and other soft tissues. The pain is usually located in one or more areas of the body, and can be triggered by a muscle strain or injury. Myofascial pain syndrome is often difficult to diagnose and may require a combination of treatments to manage the pain.
Signs and Symptoms
The primary symptom of myofascial pain syndrome is muscle pain and tenderness. The pain may be localized to one area, such as the back, neck, or shoulders, or it may be widespread and affect multiple areas of the body. Other symptoms may include muscle stiffness, weakness, headaches, and fatigue.
Causes
Myofascial pain syndrome is caused by the overuse of a particular muscle or group of muscles. This can happen when a muscle is strained or injured, or when a person performs repetitive motions, such as typing or lifting, for long periods of time.
Risk Factors
Anyone can develop myofascial pain syndrome, but some people are more likely to experience it than others. People who have jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive motions are at an increased risk, as are those who have had a recent muscle strain or injury.
Prevention
The best way to prevent myofascial pain syndrome is to practice good posture and to avoid performing repetitive motions for long periods of time. It is also important to stretch regularly, practice stress management techniques, and get enough rest.
Diagnosis
Myofascial pain syndrome is often difficult to diagnose because its symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions, such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome. To diagnose myofascial pain syndrome, a doctor may perform a physical exam, ask about the patient’s medical history, and look for trigger points in the muscles. A trigger point is an area of the muscle that is painful when pressed.
Treatment
Treatment for myofascial pain syndrome typically involves a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Physical therapy can help to strengthen and stretch the affected muscles, and lifestyle changes, such as stress management techniques, can help to reduce the pain.
Coping and Support
The pain and other symptoms associated with myofascial pain syndrome can be difficult to manage, but there are a few things that can help. Talking to a doctor or therapist can be beneficial, as can joining a support group or talking to friends and family.
Complications
If left untreated, myofascial pain syndrome can lead to chronic pain and disability. It can also cause difficulty sleeping, depression, and anxiety.
Living with Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Living with myofascial pain syndrome can be challenging, but there are a few things that can help. Practicing good posture, stretching regularly, and avoiding repetitive motions can help to reduce pain and improve quality of life. It is also important to talk to a doctor or therapist about treatment options and to seek support from family and friends.
Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic condition that can cause pain and tenderness in the muscles and other soft tissues. Symptoms include muscle pain and tenderness, stiffness, weakness, headaches, and fatigue. The condition is often caused by the overuse of a particular muscle or group of muscles and can be difficult to diagnose. Treatment typically involves a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Living with myofascial pain syndrome can be challenging, but there are a few things that can help to reduce pain and improve quality of life.