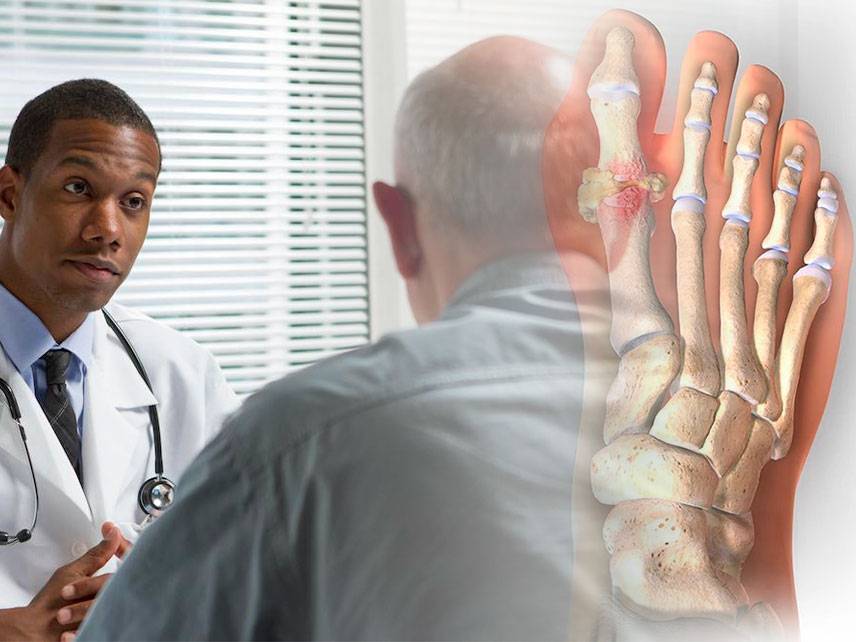
Gout is a form of arthritis that is caused by a spike in uric acid levels in the body. It is characterized by sudden, severe episodes of joint pain, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling. Gout is most common in men over the age of 40, but it can occur in both men and women of any age.
Signs and Symptoms of Gout
Gout pain typically develops suddenly, without warning, and often occurs in the middle of the night. The affected joint may be hot, swollen, and tender to the touch. In severe cases, the joint can become so swollen and tender that even the weight of a bedsheet can be unbearable. Other signs and symptoms of gout include:
-
Joint stiffness
-
Limited range of motion
-
Fatigue
-
Fever
-
Redness
-
Warmth
Causes
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a normal waste product created by the breakdown of purines, which are found in certain foods. Normally, the uric acid is dissolved in the blood and passed out of the body in the urine. However, if the body produces too much uric acid or if the kidneys do not effectively filter it out, the uric acid builds up, forming needle-like crystals in the joints. This causes inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Risk Factors of Gout
Certain lifestyle and dietary habits can increase the risk of gout. These include:
-
Eating a diet high in red meat, seafood, and certain types of alcohol
-
Being overweight
-
Having high blood pressure
-
Having certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease
-
Taking certain medications, such as diuretics or aspirin
-
Having a family history of gout
Prevention of Gout
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of gout. These include:
-
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables
-
Staying physically active
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Avoiding alcohol and certain foods high in purines
-
Drinking plenty of water
-
Avoiding certain medications, such as diuretics
Diagnosis
Gout can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be easily confused with other types of arthritis. Your doctor will likely ask about your medical and family history, do a physical exam, and order blood tests to check your uric acid levels. Your doctor may also order imaging tests, such as X-rays or an ultrasound, to get a better look at the affected joints.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. Treatment may include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or colchicine. In some cases, medications such as allopurinol may be used to reduce uric acid levels in the blood.
Coping and Support
Living with gout can be difficult, but there are several things you can do to help manage your symptoms. These include:
-
Eating a healthy diet
-
Staying physically active
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Avoiding alcohol and certain foods high in purines
-
Drinking plenty of water
-
Avoiding certain medications, such as diuretics
-
Taking medications as prescribed
-
Reducing stress
-
Joining a support group
Complications
Gout can cause complications if left untreated. These include joint damage, tophi (chalky deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints, skin, and other tissues), and kidney stones.
Living with Gout
Gout can be a difficult condition to live with, but there are several steps you can take to help manage your symptoms. Eating a healthy diet, staying physically active, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding certain foods and medications can help reduce the risk of flare-ups. Additionally, talking to your doctor about medications and lifestyle changes can help you find the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Gout is a common form of arthritis that is caused by a buildup of uric acid in the body. It is characterized by sudden, severe episodes of joint pain, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling. There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of gout, including eating a healthy diet, staying physically active, and avoiding certain foods and medications. Treatment typically includes medications to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. Additionally, making lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress and joining a support group, can help you cope with gout.