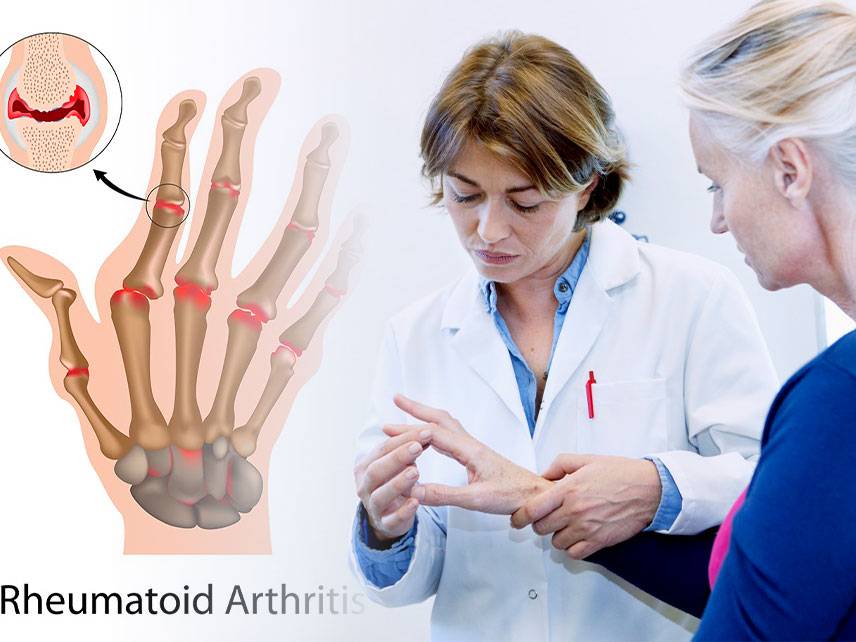
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the joints and other body systems, including the heart, lungs, eyes, and skin. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. RA typically affects the hands, feet, wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. RA can be difficult to diagnose, as symptoms can vary from person to person.
Living with Rheumatoid arthritis
Signs and Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of RA include:
-
Joint pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness
-
Joint stiffness in the morning and after inactivity
-
Joint warmth
-
Loss of joint range of motion
-
Fatigue
-
Fever
-
Weight loss
Causes
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is believed that certain viruses and bacteria can trigger an abnormal immune response in people who are genetically prone to developing RA.
Risk Factors
Certain people are more likely to develop RA than others. Risk factors for RA include:
-
Age: RA is more common among people over 40.
-
Gender: Women are more likely to develop RA than men.
-
Family history: People with a family history of RA are more likely to develop the condition.
-
Smoking: People who smoke are more likely to develop RA than non-smokers.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent RA, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding risk factors, such as smoking, may help reduce the risk.
Diagnosis
RA is diagnosed based on a person’s medical history, physical exam, laboratory tests, and imaging tests, such as X-rays. The doctor may also use blood tests to look for markers of inflammation, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP).
Treatment
Treatment for RA typically includes a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Medications used to treat RA include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic response modifiers, and corticosteroids. Lifestyle changes may include getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that may worsen symptoms.
Coping and Support
Living with RA can be challenging, but there are ways to cope with the condition. It is important to talk to family and friends about your condition and to get support from a healthcare team. There are also support groups and online communities dedicated to helping people with RA.
Complications
RA can lead to complications, including joint damage, increased risk of infection, eye problems, and heart disease. It is important to work with a healthcare team to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with RA can be difficult, but there are ways to manage the condition and improve quality of life. It is important to talk to a healthcare team about treatment options, as well as lifestyle changes that may help manage symptoms. Additionally, getting support from family and friends can be beneficial.